Medical Publications
 Discussion: Use of Auricular Composite Graft in Rib Cartilage-Based Rhinoplasty for Contracted Nose Correction
Discussion: Use of Auricular Composite Graft in Rib Cartilage-Based Rhinoplasty for Contracted Nose Correction
Received for publication September 16, 2024; accepted
September 25, 2024.
Background: Dr. Kenneth Kim, a recognized expert in Asian rhinoplasty and a well-published authority in the field, was invited by Plastic and Reconstructive Journal (PRS) to lend his expertise to a peer-reviewed publication on rhinoplasty correction for contracted noses. Dr. Kim was asked to review the study and author a Discussion piece, providing his specialized insights and professional feedback. His contribution highlights advanced techniques and considerations in addressing complex Asian rhinoplasty revisions.
 A Comprehensive Assessment of Soft-tissue Sagging
A Comprehensive Assessment of Soft-tissue Sagging
after Zygoma Reduction Surgery through Artificial
Intelligence Analysis
Received for publication March 4, 2024; accepted June 21, 2024
Background: Overdevelopment of zygomatic bones often results in protrusion and
flaring of the midfacial region. This makes the face appear squarer than the more
favorable oval shape. Therefore, zygoma reduction surgery has become a commonly performed procedure in patients seeking to obtain an ideal facial shape.
Facial soft-tissue ptosis is one of the main complications of zygoma reduction surgery. Previously, the evaluation of cheek soft-tissue ptosis was subjectively based on
patients and surgeons. Our study aimed to provide an objective evaluation of softtissue sagging in the cheek region after zygoma reduction surgery using artificial
intelligence (AI).
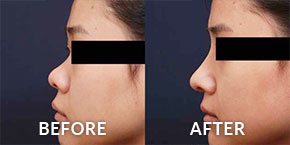
 Optimizing Esthetic Outcomes and Bone Stability:
Chin Advancement Through Inverted V
Osteotomy
Optimizing Esthetic Outcomes and Bone Stability:
Chin Advancement Through Inverted V
Osteotomy
Received February 24, 2024. Accepted for publication April 3, 2024.
Abstract: Traditional horizontal osteotomies for small and short chins often yield suboptimal results due to limited bone advancement, resulting in deep labiomental folds and heightened bone resorption risks.
 Cutaneous Layer and SMAS Suspension (CaSS) Lift
as a Minimally Invasive Lateral Midface Lift
Cutaneous Layer and SMAS Suspension (CaSS) Lift
as a Minimally Invasive Lateral Midface Lift
Received July 2, 2023. Accepted for publication September 30, 2023.
Background: In our prior study, the authors determined that pulling on the superficial adipose layer is more effective in lifting the skin than pulling on the superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS). Applying this concept of using the superficial adipose layer to transmit the lifting force to the skin, this study examined improvements in patients who underwent lateral midface lifting using our minimally invasive multilayer lifting technique and measured the duration of those improvements.
 The Rationale of Coronal Approach to Malar/Zygoma Reduction
The Rationale of Coronal Approach to Malar/Zygoma Reduction
Received for publication July 24, 2023; accepted August 16, 2023.
Background: Malar/zygoma reduction is an effective procedure to change a broader, flatter facial appearance to an oval facial shape. Of the intraoral and coronal approaches, the intraoral is the more commonly used technique than the coronal, due to the perception that complications with the coronal approach are significant, and intraoral results are satisfactory. We compared the postoperative effects of both approaches.
 American Society of Plastic Surgeons Evidence- Based Clinical Practice Guideline: Eyelid Surgery for Upper Visual Field Improvement
American Society of Plastic Surgeons Evidence- Based Clinical Practice Guideline: Eyelid Surgery for Upper Visual Field Improvement
Received for publication September 1, 2020; accepted January 19, 2022.
Background: A group of experts from different disciplines was convened to develop guidelines for the management of upper visual field impairments related to eyelid ptosis and dermatochalasis. The goal was to provide evidence- based recommendations to improve patient care.
 Subbrow Lift Using Frontalis Sling to Correct Lateral Orbital Laxity
Subbrow Lift Using Frontalis Sling to Correct Lateral Orbital Laxity
Received: 20 March 2020 / Accepted: 5 July 2020
Subbrow Lift Using Frontalis Sling to Correct Lateral Orbital Laxity
In order to correct upper lid laxity, upper blepharoplasty, subbrow excision, and forehead lift have been utilized. Our newly developed subbrow excision attaches the orbicularis oculi muscle to the frontalis mus- cle. This improves the longevity of the result without inhibiting the gliding plane of the periorbita.
The Use of a Retromammary Adipofascial Flap in Breast Augmentation for Patients with Thin Soft Tissue
Aesth Plast Surg
21 May 2018 / Accepted: 14 August 2018
The application of a retromammary adipofascial flap is an effective method of producing natural breast shape and providing additional soft tissue to the caudal breast region.
 High Double Eyelid Fold Correction Using Wide Dual-Plane Dissection
High Double Eyelid Fold Correction Using Wide Dual-Plane Dissection
Annals of Plastic Surgery, Vol. 78, No. 4
April 2017
Using a wide double-layer dissection, high folds were lowered success- fully even in situations where there was no redundant upper eyelid skin for excision. Read article for further information.
 Correction of Severely Contracted Nose
Correction of Severely Contracted Nose
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Vol. 138, No. 3
September 2016
Preoperative injection of isolated adipose- derived stromal cells into the contracted nasal scar tissue resulted in softening of the nasal enve- lope. Intraoperative release of remaining scar tis- sue and reconstruction of the internal framework with autologous grafts resulted in stable postop- erative results. There were no recurrences of con- tracture and there were no ischemic injuries to the overlying skin.
 Double-Eyelid Surgery Using Septoaponeurosis Junctional Thickening Results in Dynamic Fold in Asians
Double-Eyelid Surgery Using Septoaponeurosis Junctional Thickening Results in Dynamic Fold in Asians
PRS Global Open
May 9, 2013
The authors introduce a double-eyelid surgery technique us- ing the SAJT. This SAJT fixation technique creates a dynamic double-eyelid fold. Our study showed a high patient satisfaction rate and that the resulting fold mimics the movement of the congenital supratarsal fold in Asians.
 Effective Use of a Silicone-induced Capsular Flap in Secondary Asian Rhinoplasty
Effective Use of a Silicone-induced Capsular Flap in Secondary Asian Rhinoplasty
PRS Global Open
June 17, 2014
In secondary rhinoplasty after a silicone implant was used in the primary setting, the use of the capsular flap to preserve the dorsal SSTE volume was safe and reliable. There were no cases of recurrent capsular contracture, capsular resorption, or postoperative infection (Fig. 3). This technique avoids the dorsal irregularity and nasal SSTE vascular compromise that can occur with complete capsule removal.
 Adjunctive Techniques to Traditional Advancement Procedures for Treating Severe Blepharoptosis
Adjunctive Techniques to Traditional Advancement Procedures for Treating Severe Blepharoptosis
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Vol. 133, No. 4
April 2014
The advancement technique using the levator aponeurosis–Müller’s muscle–lamina propria mucosa of conjunctiva composite was effective in the treatment of severe blepharoptosis with levator function of 2 to 7 mm. The technique produced elevating motion of the physiologic eyelid in a superior-posterior direction. There were no serious complications, such as long-term lagophthalmos or lid lag.
 Transareolar-Perinipple (Areolar Omega) Zigzag Incision for Augmentation Mammaplasty
Transareolar-Perinipple (Areolar Omega) Zigzag Incision for Augmentation Mammaplasty
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Vol. 135, No. 3
March 2015
The transareolar-perinipple (areolar omega) zigzag incision resulted in satisfactory postoperative scarring and surgical results in Asian patients. This method increases the opening of the areolar incision and can be performed in patients with small (<3.5 cm) areolas. This approach can be an alternative in patients who are prone to hypertrophic scarring.
 Correcting Upper Eyelid Retraction By Means of Pretarsal Levator Lengthening For Complications Following Ptosis Surgery
Correcting Upper Eyelid Retraction By Means of Pretarsal Levator Lengthening For Complications Following Ptosis Surgery
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Vol. 130, No. 1
July 2012
It is very difficult to correct eyelid retraction caused by tissue fibrosis and muscle degeneration. Correction of the retraction by levator lengthening using the pretarsal tissue is simpler to execute, measurable during surgery, and easy to adjust, and offers high predictability in its result.
 Correction of Asian Short Nose With Lower Lateral Cartilage Repositioning and Ear Cartilage Grafting
Correction of Asian Short Nose With Lower Lateral Cartilage Repositioning and Ear Cartilage Grafting
PRS Global Open 2013
In our study, we have found lower lateral cartilage repositioning and ear cartilage grafting techniques to be effective in correcting short nose in Asians, with a low incidence of complications. Advantages of this technique include elongation of the entire nasal tip and ala, which results in more comprehensive and proportioned nasal augmentation. The mobile nasal tip is maintained by adequately freeing the retaining forces of the lower lateral cartilage while providing enough structural support.
 Repetitive exposure to TGF-β suppresses TGF-β type I receptor expression by differentiated osteoblasts
Repetitive exposure to TGF-β suppresses TGF-β type I receptor expression by differentiated osteoblasts
Elsevier Gene 379 (2006) 175-184
Our new findings further define a critical role for Runx2 on TβRI expression by osteoblasts, and that Runx2 may act independently of other active elements such as Sp1 that drive basal TβRI synthesis by many cells (Ji et al., 1997). They emphasize the significance of regulatory mechanisms, generated in part by TGF-β itself that can limit its own effects within the skeleton, which may occur to maintain a balanced and controlled progression of events required for proper bone remodeling. Studies like these may further improve our understanding of development and disease in other cell types where Runx2 or other Runx isoforms are expressed, and where TGF-β activity has prominent biological effects.
 Time- and Dose-Related Interactions between Glucocorticoid and Cyclic Adenosine 3*,5*– Monophosphate on CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein- Dependent Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Expression by Osteoblasts*
Time- and Dose-Related Interactions between Glucocorticoid and Cyclic Adenosine 3*,5*– Monophosphate on CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein- Dependent Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Expression by Osteoblasts*
Endocrinology Vol. 141, No. 1
2000
Our current studies continue to reveal novel interactions between PKA-activating hormones and glucocorticoids and potential mechanisms for the permissive effects of glucocorticoids on IGF-I expression and protein synthesis by osteoblasts. Future studies will be necessary to define in more detail the complex molecular events that distinguish the permissive and suppressive effects of glucocorticoids on osteoblast function and skeletal integrity .
 Runt Domain Factor (Runx)-dependent Effects on CCAAT/ Enhancer-binding Protein d Expression and Activity in Osteoblasts*
Runt Domain Factor (Runx)-dependent Effects on CCAAT/ Enhancer-binding Protein d Expression and Activity in Osteoblasts*
The Journal of Biological Chemistry
May 8, 2000
Our results predict that gene expression through these two transcription factors can occur in multiple ways. As modeled in Fig. 7A, some genes (denoted as X), including C/EBP , could be regulated directly by Runx proteins, and other genes (denoted as Y) could be regulated directly by C/EBP gene family members.
 Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Proteins Localize to Discrete Cell Culture Compartments in Periosteal and Osteoblast Cultures From Fetal Rat Bone
Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Proteins Localize to Discrete Cell Culture Compartments in Periosteal and Osteoblast Cultures From Fetal Rat Bone
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 71:351-362
1998
Similar IGFBPs are expressed by less differentiated periosteal bone cells and osteoblast-enriched cultures from fetal rat bone. Expression of IGFBP-3, IGFBP-4, and IGFBP-5 was enhanced by activators of PKA, while potent activators of PKC inhibited IGFBP-5 expression.
 Cases of Mild Ptosis Correction with Suture-Method
Cases of Mild Ptosis Correction with Suture-Method
Archives of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, Vol. 18, No. 1
2012
This article introduces the minimally invasive double eyelid surgical technique, in which a permanent suture is used in order to make the double eyelid crease and correct mild ptosis without making an incision. The advantages are minimal to no scarring, quick recovery time, and minimal trauma to the eyelid tissue. Lastly, the advantage of the present method is its technical simplicity and relatively short operating time.